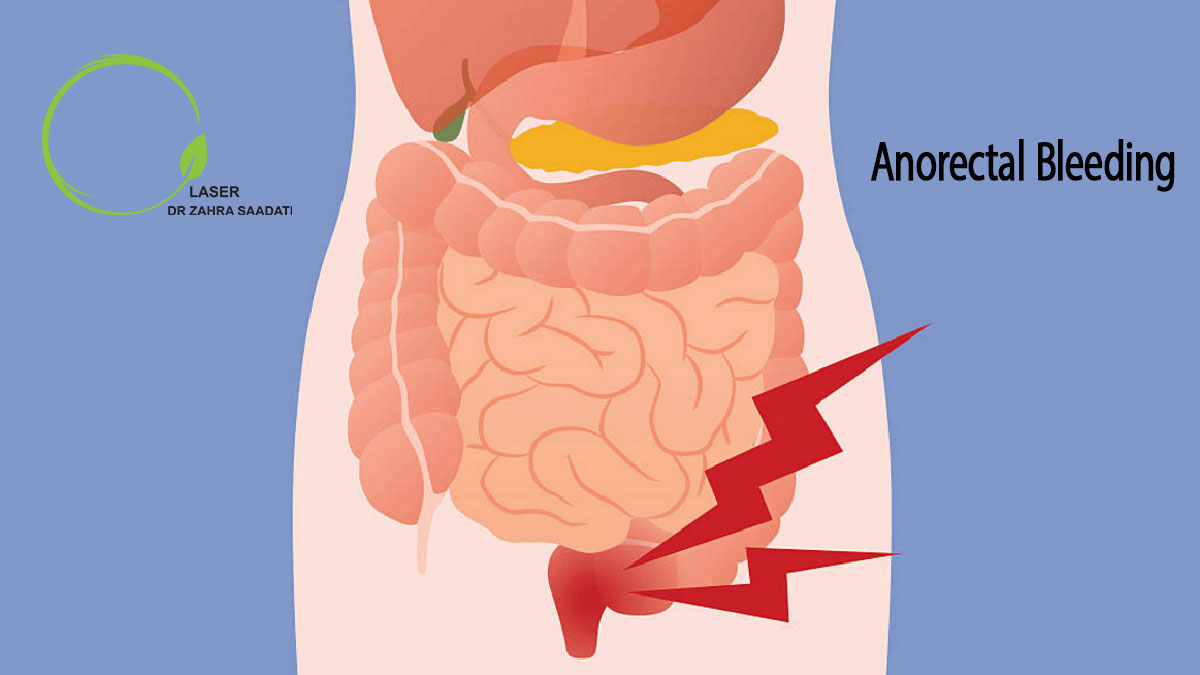
Anorectal bleeding is one of the symptoms of anal diseases. However, it is necessary to make sure that the bleeding is related to the anal area and has nothing to do with the small intestine and other areas of the gastrointestinal tract. If you have a history of gastrointestinal diseases, your anorectal bleeding is likely to be related to some areas of the gastrointestinal tract. anorectal bleeding alone, especially when you notice spots of bright red blood on the toilet paper, is usually a sign of hemorrhoids or fissures. The sole symptom of internal hemorrhoids is bleeding during defecation. Anorectal bleeding with a sense of irritation during defecation is also among the symptoms of anal fissures. If you have other symptoms along with anorectal bleeding, you should urgently visit a general surgeon.

Etiology of anorectal bleeding:
It is very important to diagnose and treat anorectal bleeding; you can visit a general surgeon to take the necessary measures for treating this condition. The general surgeon asks you questions about your symptoms, reviews your medical records, and performs the necessary examinations to determine the source of bleeding. The general surgeon may also ask questions about the history of anorectal and gastrointestinal diseases in your family.
- Color of blood, volume of bloody discharges, and type of bleeding all help the surgeon to correctly diagnose the disease. Blood from the anus and the lower part of the rectum, which is usually bright red, may occur with stool or as streaks of blood from the anus after defecation. All these are symptoms of anal fissures or internal hemorrhoids.
- Blood from the large intestine often occurs during defecation and is a little darker in color. Bleeding related to colitis, diverticulosis, and intestinal tumors share the same characteristics.
- Completely dark blood mixed with stool is a sign of duodenal ulcers.
- Heavy bleeding that changes the stool color and is accompanied by suspected abdominal pain can be a sign of colon cancer.
- The physician carefully examines the cause and volume of bleeding step by step. It is also important to determine the nature of bleeding. Other factors that can greatly help physicians to diagnose the cause of bleeding are symptoms such as fever, abdominal or stomach pain, and hard or loose stools, patient’s weight, history of diseases, medications, and internal surgeries.
- Physical examinations, such as proctoscopy, may be also performed to accurately determine the cause of anorectal bleeding. Diagnostic tests will be performed for patients aged over 40 because they are at greater risk of developing gastrointestinal cancers.
- Anal fistulas and anorectal abscesses are among the diseases that cause anorectal bleeding. In addition, anorectal bleeding accompanied by an infection can be an indication of an anal fistule.
Treatment of anorectal bleeding
Preventive and medical measures should be taken as soon as anorectal bleeding is diagnosed. In patients with hemorrhoids or an anal fissure, medication can be prescribed in the first days of observing bleeding symptoms. Note that if you visit a physician as soon as possible, you will not probably need to undergo hemorrhoid or fissure surgery. It is hence recommended to visit a general surgeon as soon as you notice a sign of anorectal bleeding.
The general surgeon may prescribe you to undergo surgery in more advanced cases. Since the anal tissue is sensitive and easily irritable, anorectal diseases are recommended to be treated through laser surgery. Click here to get more information about the advantages of laser surgery over conventional and open surgery.
Prevention of anorectal bleeding
The most important factor in preventing anorectal bleeding is to control constipation. Constipation and even severe and chronic diarrhea damage the inner wall of the anus and rectum. Moreover, spicy and allergenic foods, such as pepper, stimulates the wall of the intestine, anus, and digestive system. It is hence recommended to avoid or minimize the consumption of spicy foods and fast foods.
To prevent anorectal bleeding, it is better to drink more water and juices and eat more vegetables and high-fiber foods. A regular schedule for daily activities and exercise can also help you maintain a healthy body. All these items allow you to have a healthy lifestyle and prevent all kinds of diseases, including anorectal bleeding.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about anorectal bleeding:
1-Which medical expertise can deal with anorectal bleeding?
If the blood from your rectum is light in color, you may have hemorrhoids or an anal fissure; therefore, you should visit a general surgeon. It is recommended to find an experienced and proficient general surgeon and laser surgery specialist. If the blood from your rectum is darker, it may be related to the upper digestive system; in such cases, it is better to visit a gastroenterologist.
2-What is the cause of anorectal bleeding without defecation?
The cause of anorectal bleeding is determined based on the color of the blood. Bright red blood is usually indicative of ulcers, fissures, or thrombosed hemorrhoids. You may notice heavy bleeding without defecation when the thrombosed hemorrhoid drains by itself. Dark red or brown blood can also indicate gastrointestinal bleeding or even cancer.
3-What is the cause of painless anorectal bleeding mean?
Painless anorectal bleeding is usually among the symptoms of internal hemorrhoids. The only symptoms that patients with internal hemorrhoids or piles have are occasional bleeding or a sense of a lump in the anus. In more advanced stages, internal hemorrhoids protrude from the anus and appear as an anal skin tag. This usually occurs in internal hemorrhoids of grades 3 and 4.
4-What is the cause of anorectal bleeding after penetration?
As we know, the physiology of the anal area is not suitable for penetration; the only function of the anus is to provide easy defecation without constipation or diarrhea. Therefore, constipation, penetration, and entry of any hard object into the anus can damage the anal tissue and even cause anorectal bleeding. If you experience one of these conditions, you may first develop ulcers or fissures. If you do not treat these diseases or do not take the necessary care, you may develop other anorectal diseases such as anorectal abscesses, hemorrhoids, or even anal fistulas.